COGLAPIX

 Cross protection is a necessity in the prevention of A.p.
Cross protection is a necessity in the prevention of A.p.
|
► COGLAPIX confers cross-serotype protection against A. pleuropneumoniae. ► This effective protection, without-post vaccination reactions gives each pig the ability to breathe easily and therefore gain without pain! |
Ease of transmission, high mortality in outbreaks, frequent subclinical disease and negative impact on growth make Actinobacillus pleuropneumoniae (A.p.) an important pathogen in today’s pig farms.
We may initially observe cough, dyspnea and fever, but the painful pleuritis associated with A.p. infection has a prolonged affect on the performance of the pig.
With 15 serotypes possessing different combinations of Apx toxins, cross protection is a necessity in the prevention of A.p. At the same time, it is important to ensure that growth performance is not affected while the pig is developing protection against A.p.
 COGLAPIX is the vaccine against Actinobacillus pleuropneumoniae (A.p.).
COGLAPIX is the vaccine against Actinobacillus pleuropneumoniae (A.p.).
Coglapix® expresses all 3 Apx toxins in addition to somatic antigens of A.p.
Strains of serotypes 1 and 2 are used for the production of Apx toxins.
Coglapix® elicits a strong immune response to Apx toxoids. Vaccinated rabbits seroconverted with significant titers of anti Apx antibodies two weeks after booster.
| ELISA titers of APXI, II and III specific antibodies | ||
| Apxl titer (EU/ml) |
ApxII titer (EU/ml) |
ApxIII titer (EU/ml) |
| 50.9 | 19.2 | 10.0 |
Among somatic antigens, LPSs are of high importance in terms of immunogenicity. However the content of LPSs must be well controlled, since LPSs as endotoxins may be responsible for adverse side effect of vaccines.
Apx toxoids with a controlled amount of LPS provide the most efficient yet safe protection against pleuropneumonia caused by Actinobacillus pleuropneumoniae.
 COGLAPIX all the protection the pigs need against A. pleuropneumoniae
COGLAPIX all the protection the pigs need against A. pleuropneumoniae
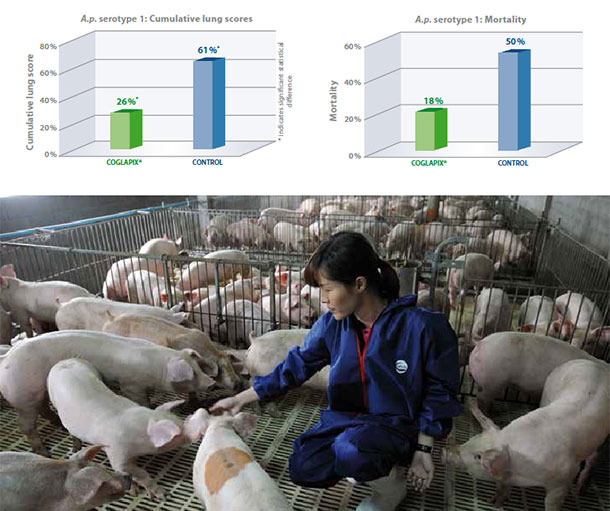
 A.p. serotype 1
A.p. serotype 1
A.p. serotype 1 produces ApxI and ApxII toxins and is therefore usually highly virulent, producing severe lung lesions and high mortality(1). In this study, A.p. seronegative pigs were vaccinated with Coglapix® at 7 and 10 weeks of age. Non vaccinated pigs served as the negative control. All animals were challenged with 5×108 CFU of a virulent A.p. serotype 1 intranasaly at 13 weeks of age and euthanized and necropsied 7 days post challenge(2).
Coglapix® vaccinated pigs had significantly lower cumulative lung scores than the non-vaccinate controls. The efficacy of Coglapix® was 77%, compared to the non-vaccinate controls, as evaluated according to Jones 2005(3), demonstrating protection against ApxI and ApxII toxins. At the same time, vaccination with Coglapix® significantly reduced the mortality after challenge with A.p. serotype 1.
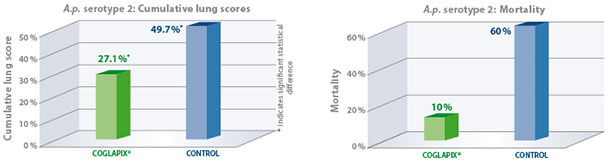
A.p. serotype 2
 Due to the expression of ApxII and ApxIII toxins, A.p. serotype 2 is highly virulent and capable of inducing strong lung lesions yet is commonly associated with low mortality(1). To determine efficacy against A.p. serotype 2, A.p. sero-negative pigs were vaccinated with Coglapix® at 6 and 10 weeks of age. Non-vaccinated pigs
Due to the expression of ApxII and ApxIII toxins, A.p. serotype 2 is highly virulent and capable of inducing strong lung lesions yet is commonly associated with low mortality(1). To determine efficacy against A.p. serotype 2, A.p. sero-negative pigs were vaccinated with Coglapix® at 6 and 10 weeks of age. Non-vaccinated pigs
served as the negative control. All animals were given a high challenge of 6×109 CFU of a virulent A.p. serotype 2 in an aerosol chamber at 13 weeks of age. The animals were euthanized and necropsied 7 days post-challenge(4).
As a result, Coglapix® protected the vaccinated animals even in these extreme challenge conditions. The vaccinated animals had significantly lower cumulative lung scores compared to controls. Vaccination with Coglapix® significantly reduced the mortality.

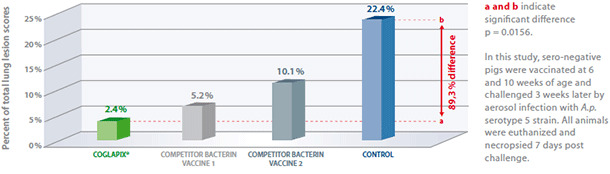
A.p. serotype 5
 Coglapix® confers protection against a heterologous A.p. serotype 5, producing ApxI and ApxII. Pigs vaccinated with Coglapix® had more resistance against infection with A.p. serotype 5, than pigs vaccinated with competitor bacterin vaccines (both containing serotype 5 bacterin antigens) and the non-vaccinated controls(4).
Coglapix® confers protection against a heterologous A.p. serotype 5, producing ApxI and ApxII. Pigs vaccinated with Coglapix® had more resistance against infection with A.p. serotype 5, than pigs vaccinated with competitor bacterin vaccines (both containing serotype 5 bacterin antigens) and the non-vaccinated controls(4).

Vaccination with Coglapix® induced more solid protection against A.p. serotype 5, compared to control and homologous bacterin vaccines.
Vaccination with Coglapix® induced significant difference: 89,3% lower lung scores.
 Coglapix® Long duration of protection
Coglapix® Long duration of protection
In modern farms, it is important to guarantee the clinical protection against Actinobacillus pleuropneumoniae until the end of the fattening period. For that purpose, duration of protection was assessed for Coglapix®.
Susceptible pigs were included in challenge studies; half of them were vaccinated twice with a 2 mL IM dose of
Coglapix®, at 3 weeks interval, the others remained as controls. At 16 weeks and 24 weeks after the 2nd vaccination, pigs were challenged by intranasal route with A.p serotype 1, 2 or 7.
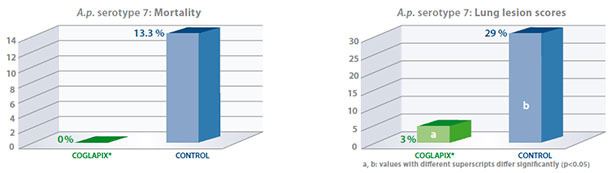
As an example, results of the serotype 7 challenge (5 x 107 cfu/pig) performed on sixty one seven-week-old
have been published(6) and are presented hereafter:
Coglapix® vaccine conferred long protection against heavy serotype 7 challenges until 34 weeks of age, considering the reduction of induced clinical signs and specific lung lesions, which are the major efficacy parameters in laboratory conditions.
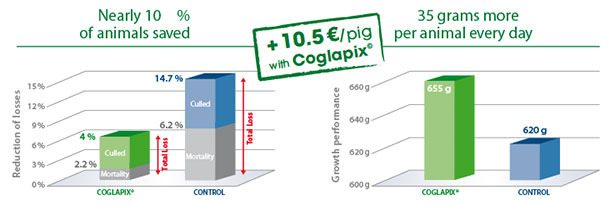
 Gain...
Gain...
16% higher profit in Coglapix® vaccinated pigs compared to unvaccinated control in farm conditions.
Effective vaccination of pigs in the nursery against Actinobacillus pleuropneumoniae with Coglapix® significantly reduces the losses due to morbidity, mortality and growth depression. In a farm with a confirmed history of A.p., a group of 493 pigs vaccinated with Coglapix® was compared to the control group of 461 non-vaccinated pigs(5).
Lower mortality and higher growth rate resulted in cumulative 16 % higher gross revenue per pig in the Coglapix® vaccinated group.
 ... without pain!
... without pain!
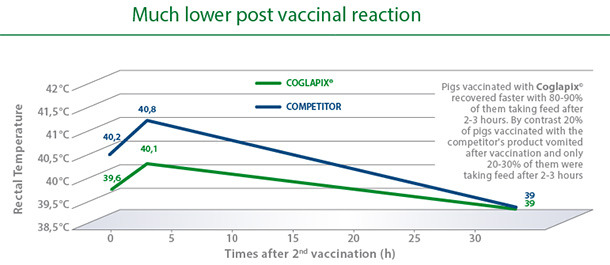
A vaccine with unique safety characteristics.
Excellent safety was confirmed under field conditions in trials comparing Coglapix® with a competitor’s subunit toxoid-OMP vaccine. Even after the second vaccination, there was only a mild elevation of body temperature after vaccination with Coglapix®. Compared to the competitor, animals vaccinated with Coglapix® had statistically significant lower rectal temperatures 1 and 3 hours after injection(4).
With Coglapix®, pigs eat while developing immunity.
References:
1 Frey J., Trends Microbiol. (1995) 3: 257-261
2 Tenk et al., 2011, 5th APVS
3 Jones et al., 2005, Swine Health Production 13:19-27
4 Ceva Internal Data
5 Krejci R et al., 2011, 5th APVS
6 Tenk M et al., 2013, 6th APVS.
Posology and method of administration: Intramuscular route. Inject one-2 ml dose according to the following schedule: two injections, 2-3 weeks apart from the age of 7 weeks. Withdrawal time: Zero days. After puncture of the stopper, use immediately. Special precautions for storage: The product must be stored between +2 and +8 °C protected from light. Do not freeze.
For more details, see the SPC applicable in your country.
This document contains information on a veterinary biological product sold in several different countries and areas where it may be marketed under different trade names and pursuant to different regulatory approvals. Accordingly, Ceva gives no guarantee that the details presented are correct with respect to all locations. In addition, the safety and efficacy data may be different depending on local regulations. Please consult your veterinarian for further information.
 Ceva Santé Animale S.A.
Ceva Santé Animale S.A.
www.ceva.com
lungprogram@ceva.com
10, av. de La Ballastière - 33500 Libourne - France - Phone: 00 33 (0) 5 57 55 40 40